Model Meaning

Product Introduction
ZWL type direct connected non clogging self-priming sewage pump integrates self-priming and non clogging sewage, adopts axial reflux form, and passes through the pump body The unique design of the impeller flow channel allows for the suction and discharge of large solid particles and long fiber impurities without the need for a bottom valve or inlet water like a typical self-priming water pump. Widely used in municipal sewage engineering, river pond manure treatment, sedimentation of waste minerals and impurities, as well as impurity pumps for chemical media such as light industry, papermaking, food, chemical industry, pharmaceuticals, electricity, paddles and mixtures.
This pump has the characteristics of simple structure, good self-priming performance (self-priming height can reach 5m), strong sewage discharge capacity, high efficiency and energy saving, and easy maintenance (can completely replace WQ and QW submersible sewage pumps). It has broad application market development prospects in the sewage pump series products
Product Features
1. Adopting a double blade impeller structure greatly improves the ability of pollutants to pass through
2. The mechanical seal adopts a new type of friction pair and operates in the oil chamber for a long time;
3. The overall structure is compact, small in size, low in noise, easy to maintain, and convenient for users to replace;
4. The automatic control cabinet can automatically control the pump's over movement and stop according to the required liquefaction changes, without the need for dedicated personnel to supervise, making it extremely convenient to use;
5. Installation methods can be provided according to user needs, which greatly facilitates installation and maintenance. People do not need to enter the sewage pit for this purpose;
6. Can be used within the design scope while ensuring that the motor does not overload;
application
ZWL type direct connected non clogging self-priming sewage pump is suitable for the discharge of severely polluted wastewater in factories and commercial areas, sewage discharge stations in main residential areas, water distribution systems in urban sewage treatment plants, drainage stations in civil air defense systems, water supply equipment in waterworks, sewage discharge in hospitals and hotels, municipal engineering construction sites, mining supporting machinery, rural biogas digesters, farmland irrigation and other industries. It can also be used for conveying granular sewage and pollutants, as well as for clean water and weakly corrosive media.
Working conditions
1. Environmental temperature ≤ 50 ℃, medium temperature ≤ 80 ℃, special requirements can reach 200 ℃
2. The pH value of the medium is 6-9 grade for cast iron and 2-13 grade for stainless steel.
3. The medium density shall not exceed 1240 kg/m3
4. The self-priming height cannot exceed the specified value of 4.5-5.5 meters, and the length of the suction pipe is ≤ 10 meters.
5. The suspended particle diameter is 60% of the pump diameter and the fiber length is 5 times the pump diameter
Structure and Working Principle Explanation
ZWL type direct connected non clogging self-priming sewage pump is mainly composed of pump body, impeller, back cover, mechanical seal, pump shaft, bearing seat, inlet valve, gas-liquid separation pipe, water inlet valve, inlet and outlet pipes, etc. The structure of the pump is shown in the diagram.
The working principle of the pump: The pump body is equipped with a liquid storage chamber, which is connected to the pump working chamber through the upper reflux hole and the lower circulation hole, forming an axial flow external mixing system of the pump. After the pump stops working, there is already a certain volume of liquid stored in the pump chamber. When the pump is started, the liquid stored in the relevant authorities is ejected upwards with air under the action of the impeller. The liquid flows back to the working chamber through the grid of the gas-liquid separation tube, and the gas is discharged outside the pump, creating a certain degree of vacuum inside the pump and achieving self-priming.
Structure diagram
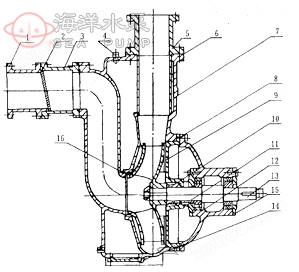 |
Serial Number |
name |
Serial number |
name |
1 |
Import takeover |
9 |
impeller |
|
2 |
Imported flange |
10 |
Mechanical seal |
|
3 |
Imported valve seat |
11 |
water deflector |
|
4 |
Water valve |
12 |
bearing |
|
5 |
discharge connection |
13 |
Pump shaft |
|
6 |
pump body |
14 |
Bearing cap |
|
7 |
Gas-liquid separation tube |
15 |
Bottom cover plate |
|
8 |
back cover |
16 |
bolt |
performance parameter
model |
internet traffic |
lift |
Motor power |
rotational speed |
efficiency |
(NPSH) Necessary corrosion allowance |
(m3/h) |
(M) |
(kw) |
(r/min) |
(%) |
(M) |
|
ZWL25-8-15 |
8 |
15 |
2.2 |
2900 |
45 |
2 |
ZWL32-10-20 |
10 |
20 |
2.2 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL40-20-15 |
20 |
15 |
2.2 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL40-15-30 |
15 |
30 |
3 |
2900 |
48 |
2.5 |
ZWL50-10-20 |
10 |
20 |
2.2 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL50-20-15 |
20 |
15 |
2.2 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL50-18-22 |
18 |
22 |
3 |
2900 |
48 |
2.5 |
ZWL50-15-30 |
15 |
30 |
3 |
2900 |
48 |
2.5 |
ZWL65-30-18 |
30 |
18 |
4 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL65-20-30 |
20 |
30 |
5.5 |
2900 |
45 |
2.5 |
ZWL65-25-40 |
25 |
40 |
7.5 |
2900 |
50 |
3 |
ZWL80-40-16 |
40 |
16 |
4 |
1450 |
50 |
3 |
ZWL80-65-25 |
65 |
25 |
7.5 |
2900 |
50 |
3 |
ZWL80-80-35 |
80 |
35 |
15 |
2900 |
45 |
3 |
ZWL80-50-60 |
50 |
60 |
22 |
2900 |
55 |
3 |
ZWL80-80-45 |
80 |
45 |
22 |
2900 |
55 |
3 |
model |
flow |
lift |
Motor power |
rotational speed |
efficiency |
(NPSH) Necessary corrosion allowance |
(m3/h) |
(M) |
(kw) |
(r/min) |
(%) |
(M) |
|
ZWL100-80-20 |
80 |
20 |
7.5 |
1450 |
53 |
4 |
ZWL100-100-15 |
100 |
15 |
7.5 |
1450 |
50 |
4 |
ZWL100-100-20 |
100 |
20 |
11 |
1450 |
53 |
4 |
ZWL100-100-30 |
100 |
30 |
22 |
2900 |
53 |
4 |
ZWL100-80-45 |
80 |
45 |
30 |
2900 |
55 |
4 |
ZWL100-80-60 |
80 |
60 |
37 |
290 |
53 |
4 |
ZWL100-80-80 |
80 |
80 |
45 |
2900 |
50 |
4 |
ZWL125-120-20 |
120 |
20 |
15 |
1450 |
55 |
4.5 |
ZWL150-200-15 |
200 |
15 |
15 |
1450 |
60 |
5 |
ZWL150-200-20 |
200 |
20 |
22 |
1450 |
60 |
5 |
ZWL150-200-28 |
200 |
28 |
30 |
1450 |
65 |
5 |
ZWL150-400-25 |
400 |
25 |
55 |
1450 |
45 |
5 |
ZWL150-180-40 |
180 |
40 |
55 |
1450 |
65 |
5 |
ZWL200-280-12 |
280 |
12 |
22 |
1450 |
62 |
5 |
ZWL200-300-18 |
300 |
18 |
37 |
1450 |
59 |
5 |
ZWL200-300-25 |
300 |
25 |
45 |
1450 |
55 |
5 |
ZWL200-280-28 |
280 |
28 |
55 |
1450 |
61 |
5 |
ZWL250-400-22 |
400 |
22 |
55 |
1450 |
65 |
5 |
ZWL300-800-14 |
800 |
14 |
55 |
1450 |
61 |
5 |
model |
internet traffic |
lift |
Motor Power |
rotational speed |
efficiency |
(NPSH) Necessary corrosion allowance |
(m3/h) |
(M) |
(kw) |
(r/min) |
(%) |
(M) |
Preparation and operation before startup
1. Check if the sturdy components of the pump base, bearings, bearing seats, and other connecting parts are loose? If there is looseness, it should be tightened.
2. Is there any jamming or abnormal noise when rotating the coupling by hand?
3. Open the water inlet valve above the pump, add no less than two-thirds of the pump body volume of stored liquid water, and close the valve. In the future, there will be no need to refill water when starting up.
4. Connect the power supply and try to turn it on. When looking at the motor end, it turns clockwise. (Reverse is strictly prohibited)
5. Turn on the machine and observe if the pump is running normally? If there are any abnormal phenomena, the cause should be identified and eliminated.
Fault analysis and troubleshooting methods
fault |
reason |
Troubleshooting |
The pump is not producing water |
1. No fluid storage or insufficient fluid storage in the pump body 2. Air leakage in the suction pipeline 3. Voltage too low 4. The suction distance is too high or the suction pipeline is too long 5. Excessive mechanical seal leakage |
1. Add enough 2. Eliminate the phenomenon of pipeline leakage 3. Adjust voltage 4. Reduce suction or shorten the pipeline 5. Repair or replace |
Insufficient pump water output |
1. Due to improper use, the impeller passage or suction pipe is blocked 2. Severe impeller wear 3. Insufficient power, too low speed |
1. Eliminate blockages 2. Replace the impeller 3. Adjust to rated speed |
Excessive pump noise and vibration |
1. Unstable footing 2. Severe bearing wear 3. Pump and motor spindle have different axes |
1. Reinforcement 2. Replace bearings 3. Adjust coaxiality |
The bearing temperature is too high |
1. Lubrication refers to deterioration or dryness 2. Bearing damage |
1. Replace the lubricating grease 2. Replace |
Pump leakage |
1. Loose connecting bolts 2. Seal wear |
1. Secure tightly 2. Replace |

